Introduction to Cybersecurity Guides
In today’s hyper-connected digital world, cybersecurity guides are no longer optional—they are essential. Every day, individuals and businesses rely on the internet for communication, banking, shopping, work, and entertainment. At the same time, cybercriminals are becoming more advanced, using automation, artificial intelligence, and social engineering to exploit security gaps. This is why well-structured cybersecurity guides exist: to help users understand digital risks and apply proven protection strategies.
A cybersecurity guide is a practical and educational resource that explains how cyber threats work, how attacks happen, and what steps you can take to protect yourself online. Unlike scattered tips or short blog posts, cybersecurity guides provide a complete roadmap—from basic online safety concepts to advanced cybersecurity best practices. Whether you are a beginner or a business owner, following reliable cybersecurity guides significantly reduces your exposure to cyber threats.http://bestbuygeeksquads.com
Recent cybersecurity research shows that global cybercrime costs are projected to exceed $10 trillion annually by 2026, making cybercrime one of the most costly global risks. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, identity theft, and online fraud are now daily occurrences. Many of these attacks succeed not because of weak technology, but because users lack awareness. Cybersecurity guides bridge this gap by turning complex security concepts into easy-to-follow actions.
Who Are Cybersecurity Guides For?
Cybersecurity guides are designed for everyone, not just IT professionals. Cybercriminals do not discriminate; they target anyone with valuable data or access to systems.
Cybersecurity guides are especially valuable for:
- Everyday internet users who want to protect personal data
- Home users securing Wi-Fi networks and personal devices
- Small business owners with limited IT security resources
- Remote workers accessing cloud platforms and company systems
- Students and beginners learning cybersecurity fundamentals
A common misconception is that hackers only target large organizations. In reality, studies show that over 40% of cyberattacks are aimed at small businesses and individual users because they often lack strong cybersecurity defenses. Cybersecurity guides help reduce this risk by providing clear, actionable guidance.
What You Will Learn From This Cybersecurity Guide
This comprehensive cybersecurity guide is structured to move step by step—from understanding core concepts to applying real-world cybersecurity solutions. The goal is to educate without overwhelming, using simple language and practical examples.
By the end of this guide, you will understand:
- What cybersecurity means in real-world terms
- The most common cyber threats affecting users today
- Essential cybersecurity best practices
- How to protect devices, data, and online accounts
- Cybersecurity strategies for home users and businesses
- How to detect and respond to cyber incidents early
To improve clarity and usability, this guide includes:
- Short, easy-to-scan paragraphs
- Bullet-point summaries
- Real-world examples and mini case studies
- Data-backed insights and expert recommendations
- Beginner-friendly explanations
Why Cybersecurity Guides Matter More Than Ever
Cybersecurity is not a one-time task—it is an ongoing process. As technology evolves, cyber threats evolve with it. New vulnerabilities appear with software updates, new devices, and changing work environments. Following updated cybersecurity guides ensures you stay informed, prepared, and proactive.
“Cybersecurity is not just an IT issue; it is a business and personal responsibility.”
— Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
The purpose of this cybersecurity guide is simple: to help you stay safe, confident, and in control online. In the next section, we’ll explore what cybersecurity guides actually are and why they play such a critical role in modern digital life.
What Are Cybersecurity Guides and Why Are They Important?
Cybersecurity guides are structured educational resources that explain how to protect digital systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. They combine technical knowledge, best practices, and real-world examples to help users understand what can go wrong online and how to prevent it. Unlike short tips or generic advice, cybersecurity guides provide a complete framework for staying safe in an increasingly dangerous digital environment.
At their core, cybersecurity guides focus on three main areas: prevention, detection, and response. Prevention teaches users how to avoid attacks in the first place. Detection helps identify threats early before serious damage occurs. Response explains what actions to take if a cyber incident happens. Together, these elements form a strong defense against cybercrime.
Cybersecurity guides are important because modern cyberattacks are no longer random or unsophisticated. Attackers carefully study human behavior, software weaknesses, and system misconfigurations. Even a single mistake—such as clicking a malicious link or using a weak password—can lead to data theft, financial loss, or system compromise. Cybersecurity guides exist to reduce these risks by educating users before an attack happens.
How Cybersecurity Guides Help Protect Users
One of the biggest advantages of cybersecurity guides is that they turn complex cybersecurity concepts into practical actions. Instead of overwhelming users with technical jargon, they explain risks in plain language and offer step-by-step solutions.
Cybersecurity guides help users:
- Understand how cyberattacks actually work
- Identify common warning signs of threats
- Learn safe online behaviors
- Apply security best practices consistently
- Reduce reliance on guesswork or assumptions
For example, a user might believe antivirus software alone is enough. A cybersecurity guide explains why layered security—using antivirus, firewalls, strong passwords, and updates together—is far more effective.
Cybersecurity Guides vs Cybersecurity Tools
Many people confuse cybersecurity guides with cybersecurity tools, but they serve very different purposes.
| Cybersecurity Guides | Cybersecurity Tools |
|---|---|
| Educate users | Actively protect systems |
| Explain threats and risks | Detect or block attacks |
| Teach best practices | Enforce security rules |
| Improve user awareness | Automate protection |
Cybersecurity guides teach you what to do and why, while tools help enforce those actions. The most secure environments use both. Without guidance, even the best tools can be misconfigured or misused.
Why Cybersecurity Guides Are Essential Today
The digital landscape has changed dramatically in recent years. Cloud computing, remote work, online banking, and smart devices have increased convenience—but they have also expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals.
Consider these facts:
- 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error
- A ransomware attack occurs every 11 seconds worldwide
- Phishing accounts for over 80% of reported security incidents
These numbers highlight a critical truth: technology alone cannot solve cybersecurity problems. Users must understand how threats work and how their actions affect security. Cybersecurity guides address this gap by focusing on education and awareness.
Why Cybersecurity Guides Matter for Businesses and Individuals
For individuals, cybersecurity guides help protect:
- Personal data
- Online accounts
- Financial information
- Digital identity
For businesses, cybersecurity guides help:
- Prevent data breaches
- Protect customer information
- Reduce downtime and financial loss
- Meet compliance and regulatory requirements
A real-world example illustrates this clearly.
Case Study: Small Business Email Breach
A small company suffered a financial loss after an employee clicked a phishing email disguised as an invoice. The attacker gained access to the email account and redirected payments. A basic cybersecurity guide covering phishing awareness and email verification could have prevented the incident entirely.
This example shows why cybersecurity guides are not optional reading—they are risk-reduction tools.
The Role of Cybersecurity Guides in Long-Term Online Safety
Cybersecurity is not static. New threats emerge constantly, and attackers adapt quickly. Cybersecurity guides help users stay informed, adaptable, and proactive rather than reactive.
By following updated cybersecurity guides, users can:
- Adjust security habits as threats evolve
- Stay ahead of new attack techniques
- Build a long-term security mindset
- Reduce stress and uncertainty online
In short, cybersecurity guides empower users with knowledge. And in cybersecurity, knowledge is one of the strongest defenses.
Common Cybersecurity Threats You Should Know About
Understanding cyber threats is a core part of all effective cybersecurity guides. You cannot protect yourself from dangers you don’t recognize. Cybercriminals use many different techniques, but most attacks fall into a few major categories. These threats affect individuals, home users, small businesses, and large organizations alike.
Modern cyberattacks are designed to be stealthy, fast, and psychologically manipulative. Instead of breaking systems directly, attackers often trick users into giving away access. This is why awareness is just as important as technology in cybersecurity protection.
Below are the most common cybersecurity threats explained clearly and practically.
Malware and Viruses
Malware is a broad term used in cybersecurity guides to describe any malicious software designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to systems. Malware often enters devices through infected downloads, email attachments, fake software updates, or compromised websites.
Common types of malware include:
- Viruses – Attach themselves to files and spread when opened
- Worms – Spread automatically across networks
- Spyware – Secretly monitors user activity
- Trojans – Disguised as legitimate software
- Ransomware – Encrypts files and demands payment
Malware can cause serious damage, such as slowing systems, stealing personal data, or locking users out of important files. According to cybersecurity reports, over 560,000 new malware samples are detected every day, showing how quickly threats evolve.
Warning signs of malware infection include:
- Sudden system slowdowns
- Frequent crashes or pop-ups
- Unknown programs running
- Unexpected data usage
Cybersecurity guides strongly recommend using updated antivirus software and avoiding downloads from untrusted sources to reduce malware risks.
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing is one of the most dangerous and widespread cyber threats today. It relies on tricking users rather than hacking systems. Attackers impersonate trusted organizations to steal passwords, financial data, or login credentials.
Phishing attacks commonly appear as:
- Fake emails pretending to be banks or companies
- SMS messages asking to verify accounts
- Fake login pages that look real
- Social media messages from “known contacts”
According to industry data, phishing is responsible for more than 80% of reported security incidents worldwide. Even experienced users can fall victim because phishing messages are becoming more convincing.
Cybersecurity guides teach users to:
- Verify sender email addresses
- Avoid clicking unknown links
- Never share passwords via email or SMS
- Look for spelling or formatting errors
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is one of the most feared cyber threats discussed in cybersecurity guides. It encrypts files and demands payment—often in cryptocurrency—to restore access. Victims include individuals, hospitals, schools, and businesses.
Key facts about ransomware:
- Attacks occur every few seconds globally
- Payments do not guarantee file recovery
- Backups are the most effective defense
Case Study: Healthcare Ransomware Attack
A hospital system was forced offline for days after a ransomware attack encrypted patient records. Emergency services were disrupted, and recovery costs exceeded millions. The attack succeeded due to outdated systems and poor backup practices—both preventable with proper cybersecurity guidance.
Cybersecurity guides emphasize regular backups, software updates, and restricted access as critical defenses against ransomware.
Password Attacks and Credential Theft
Weak passwords remain one of the biggest cybersecurity risks. Attackers use automated tools to guess or reuse stolen passwords across multiple platforms.
Common password-based attacks include:
- Brute force attacks – Trying many password combinations
- Credential stuffing – Using leaked passwords from other breaches
- Keylogging – Recording keystrokes secretly
Research shows that over 60% of people reuse passwords across multiple accounts, which dramatically increases risk. Cybersecurity guides strongly advise using password managers and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Why Knowing These Threats Matters
Each cyber threat targets a different weakness—technology, human behavior, or system configuration. Cybersecurity guides help users recognize these patterns and respond correctly.
Understanding threats helps you:
- Avoid dangerous online behavior
- Identify attacks early
- Reduce financial and data loss
- Build long-term security habits
Awareness is the first layer of defense. Once you understand how attacks happen, protecting yourself becomes far easier.
Cybersecurity Guides for Beginners
For beginners, cybersecurity can feel confusing and overwhelming. Many people believe cybersecurity is highly technical or only meant for IT professionals. In reality, cybersecurity guides for beginners focus on simple habits and awareness, not complex tools or coding skills. Most cyberattacks succeed because of basic mistakes, not advanced hacking techniques.
Beginner-focused cybersecurity guides aim to build a strong foundation. They explain how online threats work, what behaviors increase risk, and how small changes can dramatically improve online safety. Learning cybersecurity basics early helps prevent identity theft, account takeovers, and data loss.
Cybersecurity Basics Everyone Should Know
Every beginner cybersecurity guide starts with a few core concepts. These ideas appear in nearly all cybersecurity guides because they form the backbone of online security.
Key cybersecurity basics include:
- Confidentiality – Keeping information private
- Integrity – Ensuring data is not altered without permission
- Availability – Making sure systems and data are accessible when needed
Together, these principles are known as the CIA Triad, a fundamental concept in cybersecurity education.
Another essential concept is understanding the difference between threats, vulnerabilities, and risks:
- A threat is a potential danger (like malware)
- A vulnerability is a weakness (like outdated software)
- A risk is the chance a threat exploits a vulnerability
Cybersecurity guides help beginners see how everyday actions—such as skipping updates or using weak passwords—create vulnerabilities that attackers exploit.
Simple Cybersecurity Tips for Everyday Users
Beginner cybersecurity guides focus heavily on habits because habits determine security outcomes. You don’t need expensive tools to improve security—simple actions go a long way.
Essential cybersecurity tips for beginners:
- Use strong, unique passwords for each account
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible
- Keep operating systems and apps updated
- Avoid clicking links from unknown emails or messages
- Install apps and software only from official sources
According to cybersecurity studies, over 90% of successful cyberattacks begin with a phishing email or human error. This shows why basic awareness is one of the most powerful security tools available.
Understanding Antivirus, Firewalls, and Encryption
Many beginners hear these terms but don’t fully understand them. Cybersecurity guides break them down in simple language.
| Term | What It Does | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Antivirus | Detects and removes malware | Protects against known threats |
| Firewall | Blocks unauthorized network access | Prevents attackers from reaching your system |
| Encryption | Scrambles data so it can’t be read | Protects sensitive information |
These tools work best when combined with safe user behavior. Cybersecurity guides emphasize that tools alone are not enough—user awareness is equally important.
Common Beginner Cybersecurity Mistakes
Cybersecurity guides often highlight mistakes to help beginners avoid them. Recognizing these early can prevent serious security incidents.
Common mistakes include:
- Reusing passwords across multiple sites
- Ignoring software updates
- Trusting unknown email attachments
- Using public Wi-Fi without protection
- Assuming “nothing will happen to me”
“Attackers don’t break in—they log in.”
— Cybersecurity Awareness Quote
This quote highlights why beginners should focus on protecting credentials and access.
Why Beginners Should Follow Cybersecurity Guides Early
Cybersecurity habits are easier to build early than to fix after a breach. Once personal data is stolen, recovery can be costly, stressful, and time-consuming. Cybersecurity guides help beginners develop safe digital habits that last a lifetime.
Benefits of following beginner cybersecurity guides include:
- Reduced risk of identity theft
- Better control over online accounts
- Increased confidence using digital services
- Long-term online safety
By mastering the basics, beginners lay the groundwork for more advanced cybersecurity practices later.
Essential Cybersecurity Best Practices
All effective cybersecurity guides emphasize best practices because they form the foundation of strong digital security. These practices are not complex or expensive. Instead, they focus on consistency, awareness, and smart decision-making. When followed correctly, cybersecurity best practices significantly reduce the chances of successful cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity is most effective when it is layered. This means combining multiple protective measures so that if one layer fails, others still protect your data. Best practices apply to individuals, home users, and businesses alike.
How to Create Strong and Secure Passwords
Passwords are often the first and weakest line of defense. Many cybersecurity breaches occur because users rely on short, predictable, or reused passwords. Cybersecurity guides consistently highlight password security as a top priority.
Best practices for strong passwords include:
- Use at least 12–16 characters
- Combine uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols
- Avoid personal information such as names or dates
- Never reuse passwords across accounts
Using a password manager is one of the most effective recommendations in modern cybersecurity guides. Password managers generate, store, and autofill strong passwords securely.
Fact: Studies show that 80% of hacking-related breaches involve compromised passwords.
The Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than just a password. This could be a code sent to your phone, a fingerprint, or a hardware key.
Cybersecurity guides strongly recommend enabling MFA because:
- Stolen passwords alone are no longer enough to access accounts
- MFA blocks most automated attacks
- It significantly reduces account takeover risks
Even if attackers obtain your password, MFA can stop them from logging in.
Keeping Software and Devices Updated
Outdated software is one of the most common vulnerabilities exploited by attackers. Cybercriminals actively search for systems that have not installed security updates.
Cybersecurity guides advise users to:
- Enable automatic updates for operating systems
- Regularly update browsers, apps, and plugins
- Remove unused software
Real-world data: Over 60% of breaches involve unpatched vulnerabilities. Updates often contain critical security fixes that close known attack paths.
Safe Internet Browsing Practices
Browsing the internet safely is a recurring topic in cybersecurity guides. Many attacks occur simply because users visit unsafe websites or download malicious files.
Safe browsing best practices include:
- Look for HTTPS in website addresses
- Avoid downloading files from unknown sources
- Be cautious with free software and browser extensions
- Never ignore browser security warnings
Cybersecurity guides stress that convenience should never come at the cost of security.
Email Security Best Practices
Email remains the most common attack vector for cybercriminals. Phishing emails are designed to appear legitimate and urgent.
Cybersecurity guides recommend:
- Verifying sender email addresses
- Avoiding urgent or threatening messages
- Not clicking links without checking the destination
- Reporting suspicious emails
“Think before you click” is one of the most repeated messages in cybersecurity education—and for good reason.
Why Best Practices Matter More Than Tools Alone
Security tools are important, but they are only effective when used correctly. Cybersecurity guides emphasize that human behavior is often the weakest link in security.
By following cybersecurity best practices:
- You reduce exposure to threats
- You make attacks more difficult
- You protect both data and devices
- You build long-term digital resilience
Cybersecurity best practices are not about fear—they are about control and confidence in the digital world.
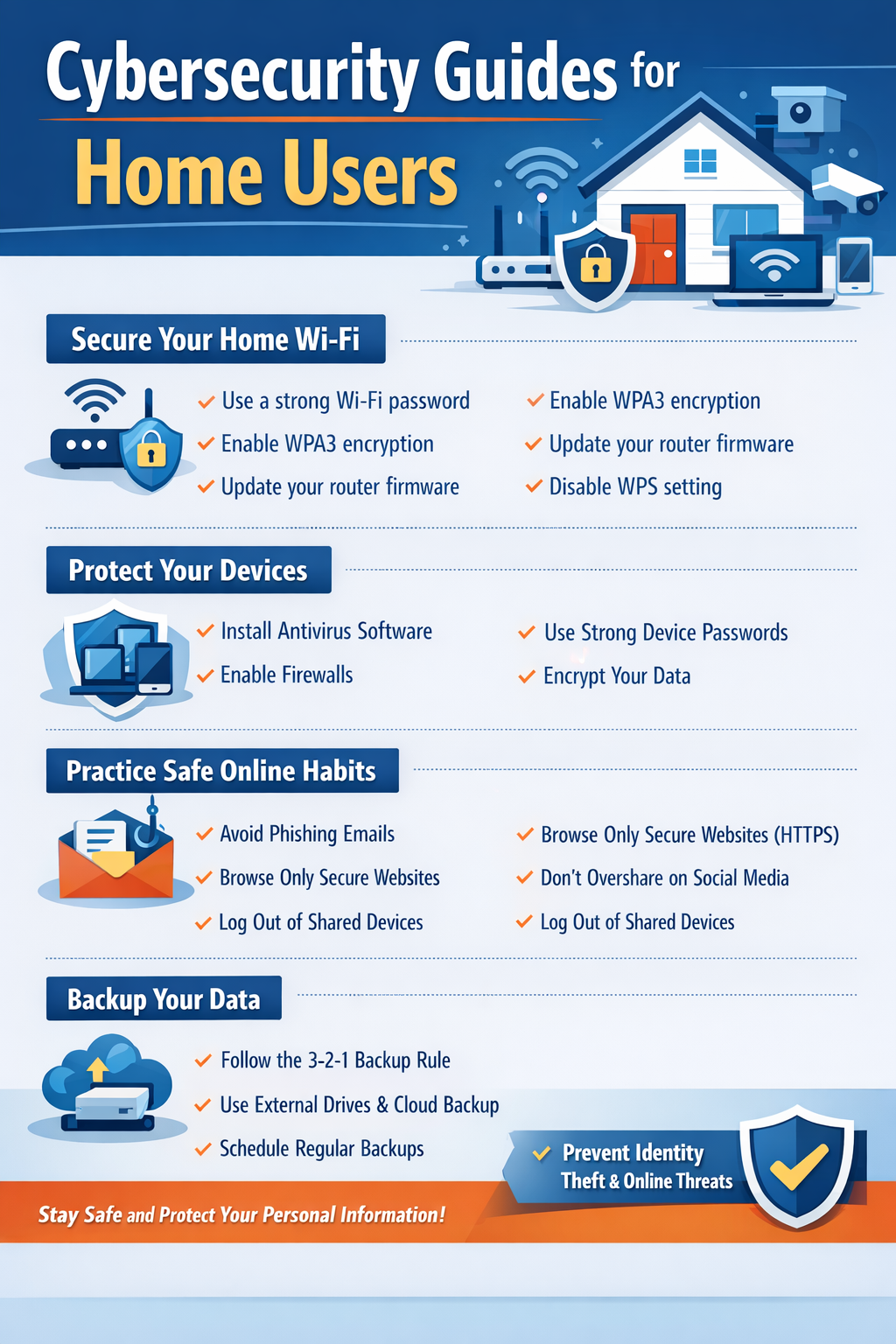
Cybersecurity Guides for Home Users
Home users are increasingly at risk in the modern digital landscape. With laptops, smartphones, smart TVs, IoT devices, and Wi-Fi networks all connected, the attack surface for cybercriminals has expanded dramatically. Many home users believe they are too small or insignificant to be targeted—but the reality is very different. Cybercriminals actively target home networks because they are often less protected than corporate systems.
Cybersecurity guides provide home users with practical, easy-to-implement strategies to protect devices, personal data, and privacy. Following these guides helps prevent identity theft, ransomware, and financial loss.
Securing Home Wi-Fi Networks
Your home Wi-Fi is the gateway to all your devices. An unsecured network can allow attackers to intercept data, steal passwords, or access connected devices.
Cybersecurity best practices for home Wi-Fi include:
- Change the default router username and password
- Use strong encryption protocols (WPA3 recommended)
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) for extra security
- Regularly update router firmware
- Hide your network SSID if possible
A strong, well-configured Wi-Fi network is one of the most important steps any home user can take. According to cybersecurity reports, over 50% of home network attacks exploit weak Wi-Fi security settings.
Protecting Personal Devices
Devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets are primary targets for cybercriminals. Home users must ensure their devices are properly secured.
Essential device protection steps recommended in cybersecurity guides:
- Install antivirus or anti-malware software
- Enable device firewalls
- Use device passwords or biometrics
- Encrypt sensitive files
- Regularly back up data (locally and to the cloud)
For IoT devices, such as smart speakers, thermostats, and cameras, ensure they are updated regularly and use unique passwords. Many smart devices ship with default passwords that are easily guessed by attackers.
Safe Online Behavior at Home
Cybersecurity guides emphasize that human behavior is as important as technology. Home users should adopt safe online habits to reduce risk.
Practical advice includes:
- Avoid clicking unknown links or attachments in emails
- Use secure websites (look for HTTPS)
- Don’t share personal information on unsecured platforms
- Log out of accounts on shared devices
- Monitor accounts for suspicious activity
Backups and Data Protection
Even with all security measures in place, data loss can occur due to hardware failure, ransomware, or accidental deletion. Cybersecurity guides recommend a 3-2-1 backup strategy:
- Keep three copies of data
- Store them on two different media types
- Keep one copy offsite or in the cloud
This approach ensures data can be restored in the event of any incident.
Why Cybersecurity Guides Are Crucial for Home Users
Home users often underestimate the risks they face. Following a cybersecurity guide helps users:
- Protect sensitive personal information
- Reduce the risk of identity theft
- Prevent malware infections and ransomware attacks
- Maintain long-term online safety and peace of mind
Cybersecurity guides are not about fear—they are about empowering home users to take control of their digital environment.